PSP Architects India
Project Title: Residence for Sridhar and Pushkala
Client: NP Sridhar
City: Bangalore, India
Project Description
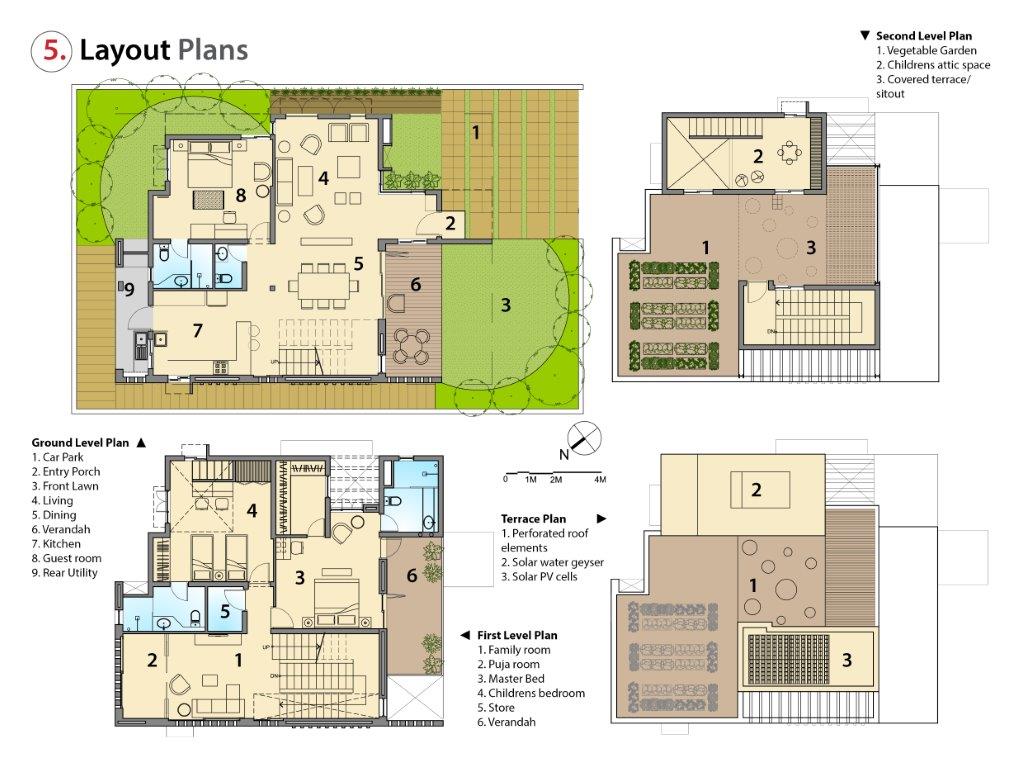
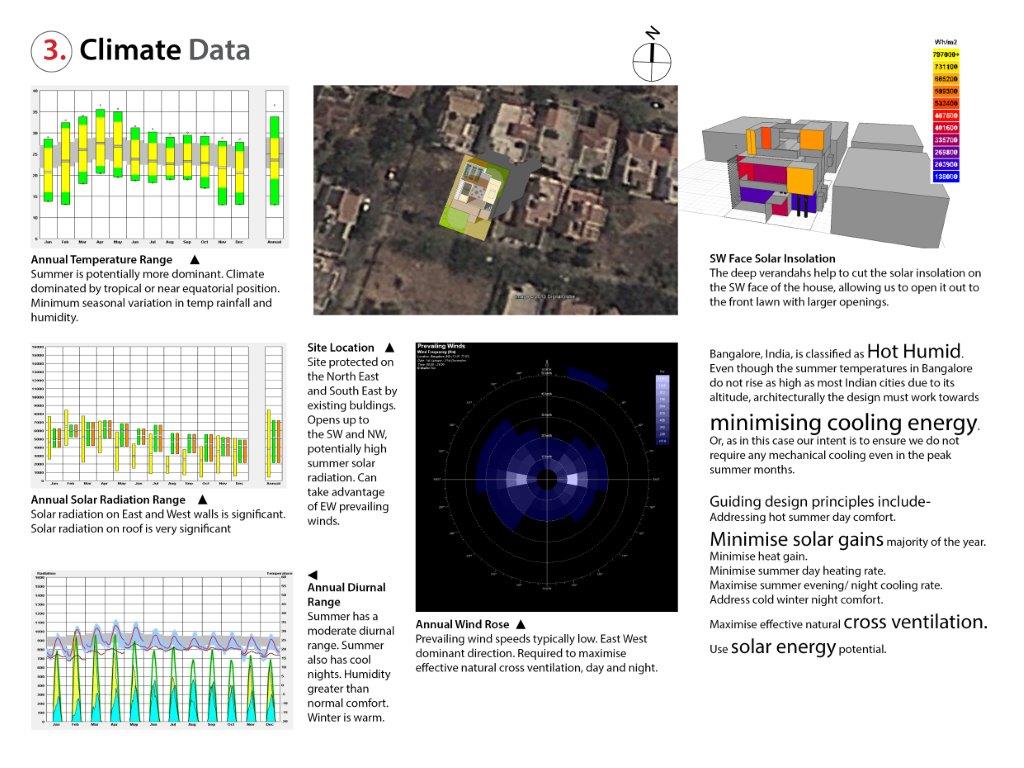
The residence is designed for a family of 4 in a gated community in Bangalore, India’s IT hub and home to a large population of “techies.” The climate is Tropical Humid Equatorial. However due to its altitude of 920m above sea level it is one of the more comfortable Indian cities with a short summer and extended moderate to cool weather. Our goal is to avoid any mechanical cooling during the short summer season by ensuring natural ventilation, shaded surfaces and openings and insulated walls.
Sustainability concept
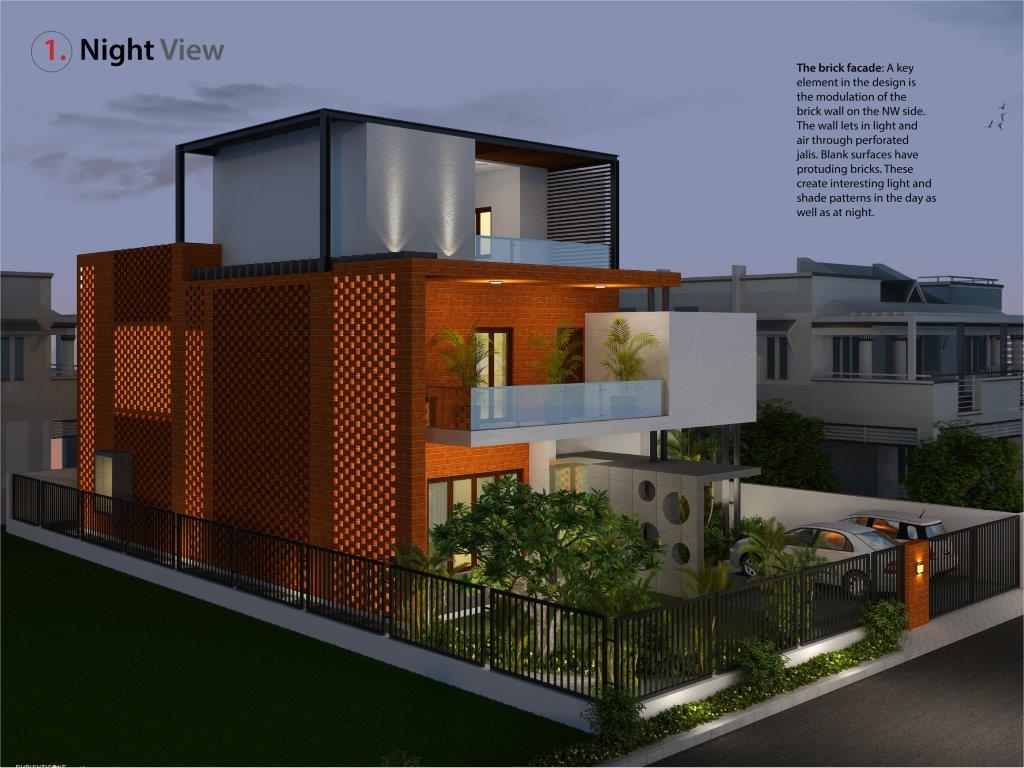
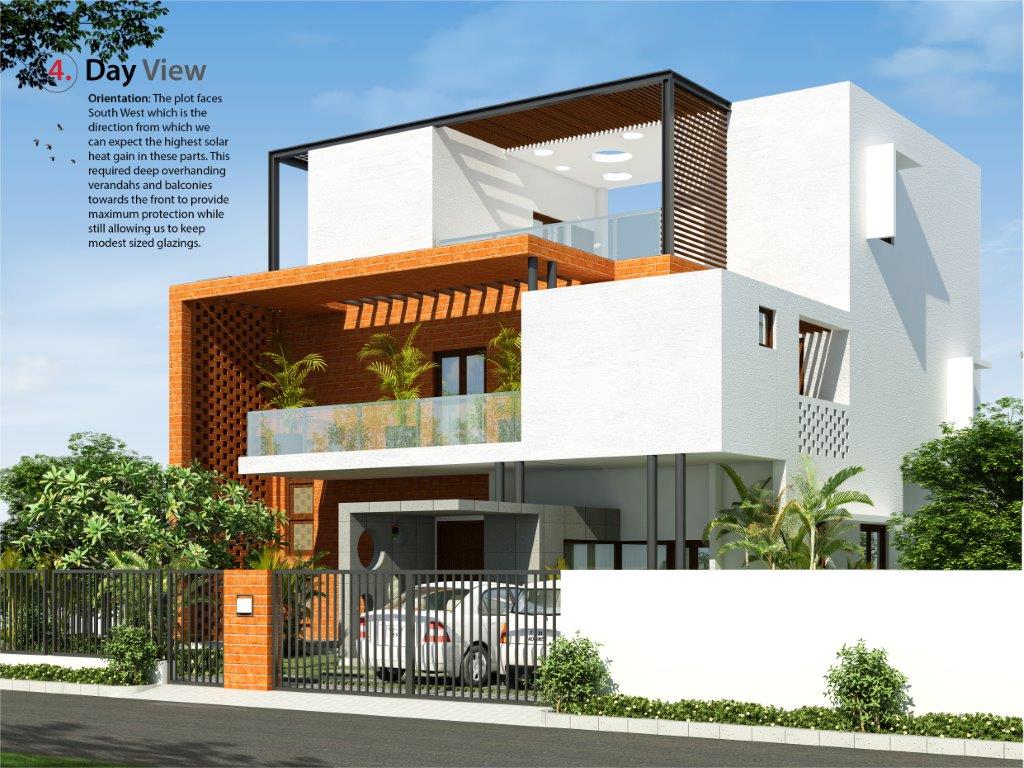
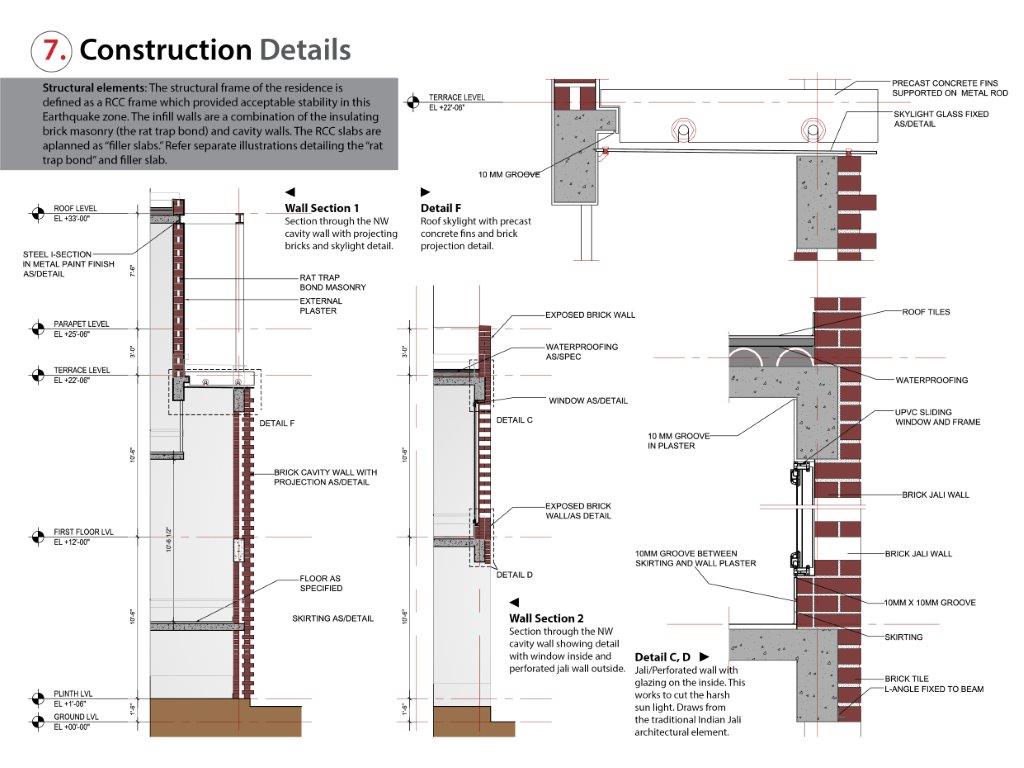
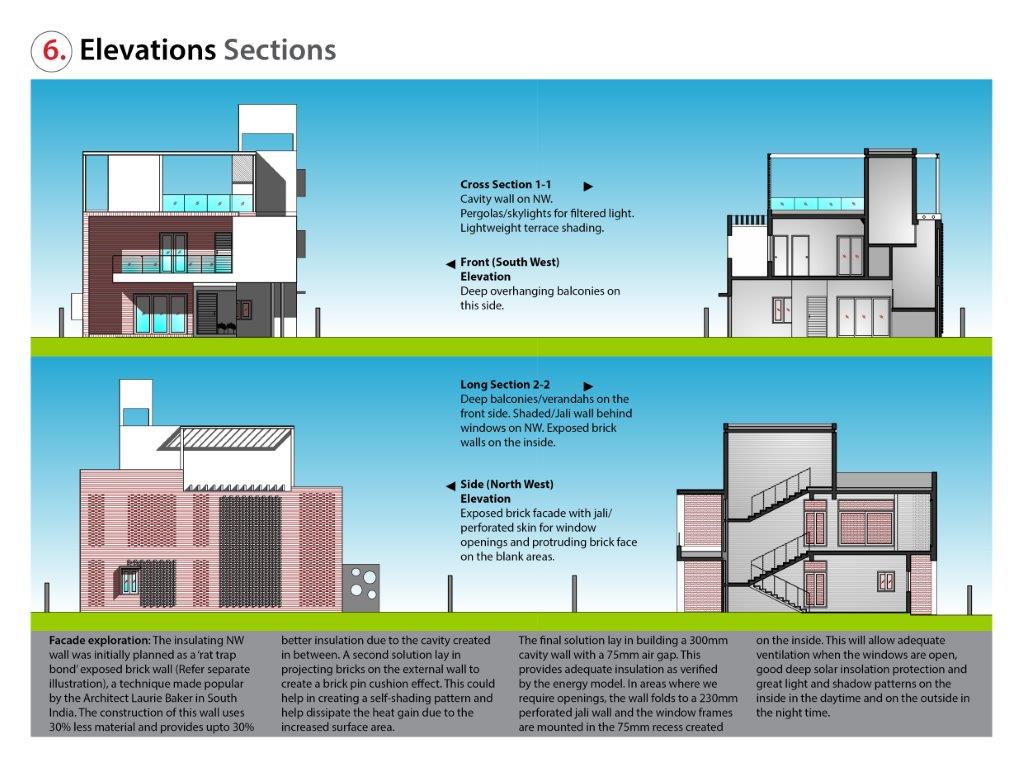
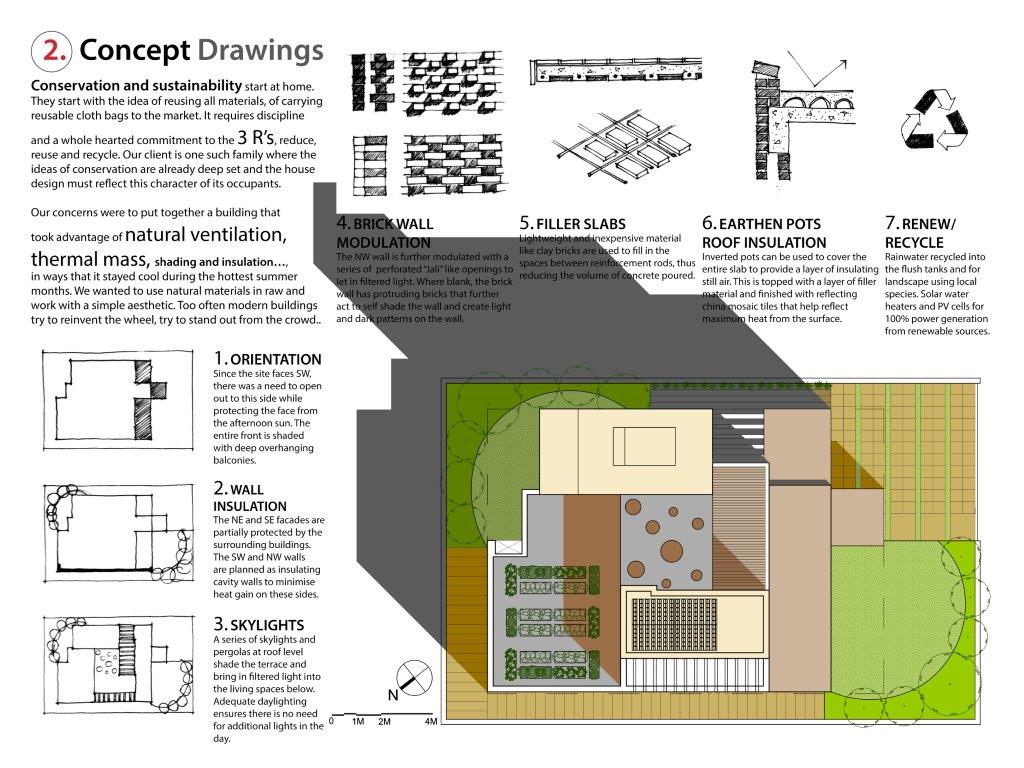
Orientation: Severe solar radiation from the SW and NW countered by deep overhanging balconies on the SW and an exposed brick cavity wall on the NW with projecting bricks to enhance self-shading and greater heat dissipation. Windows protected with a brick Jali wall (traditional Indian screen wall), which allows adequate ventilation, sun protection and interesting light and shadow effects.
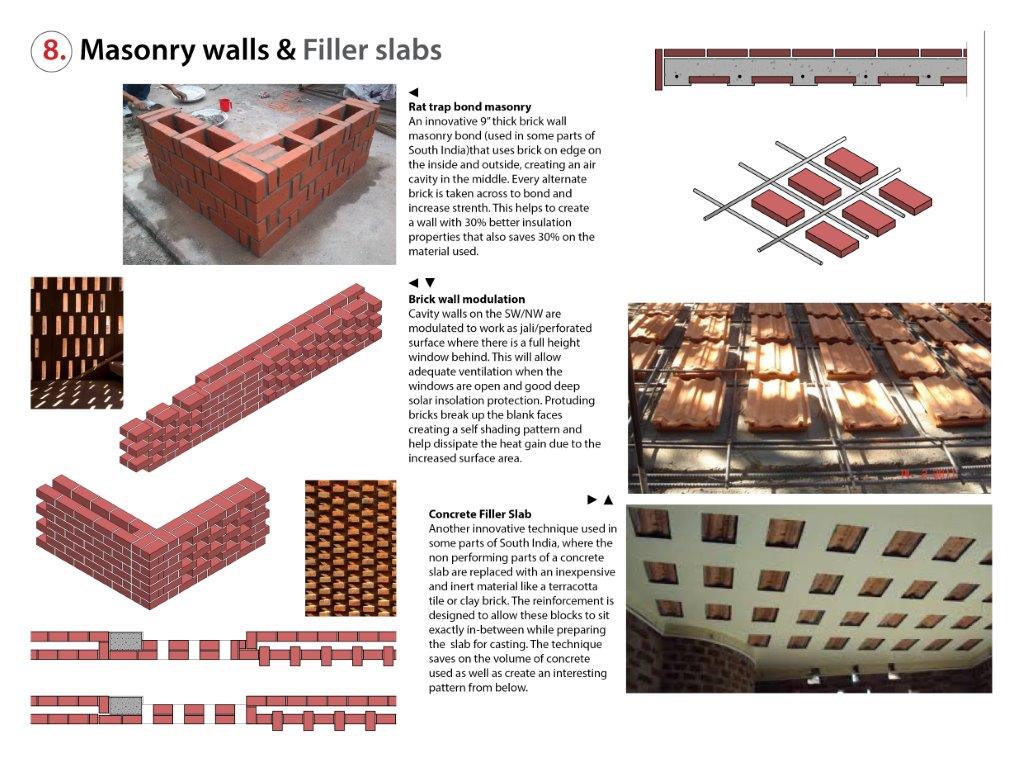
Structural: RCC frame with brick “cavity walls” and “rat trap bond” walls. RCC “filler slab” where reinforcement rods are spaced to allow placement of a filler material (brick tile) between rods to reduce volume of concrete poured and create an interesting self-pattern visible from below.
Over deck: Major heat gain to be avoided by using inverted earthen pots, inexpensive and locally available to create an air cavity above the slab.
Floor: Atangudi tiles, a beautiful tile sourced from a particular village by the same name, utilizing traditional knowledge and laying/polishing skills but imbibed with a modern colour palette/sensibility. Also a cement “cut and polish” floor, mixed with marble powder (traditionally cool floors) and titanium di oxide (bleaching agent).
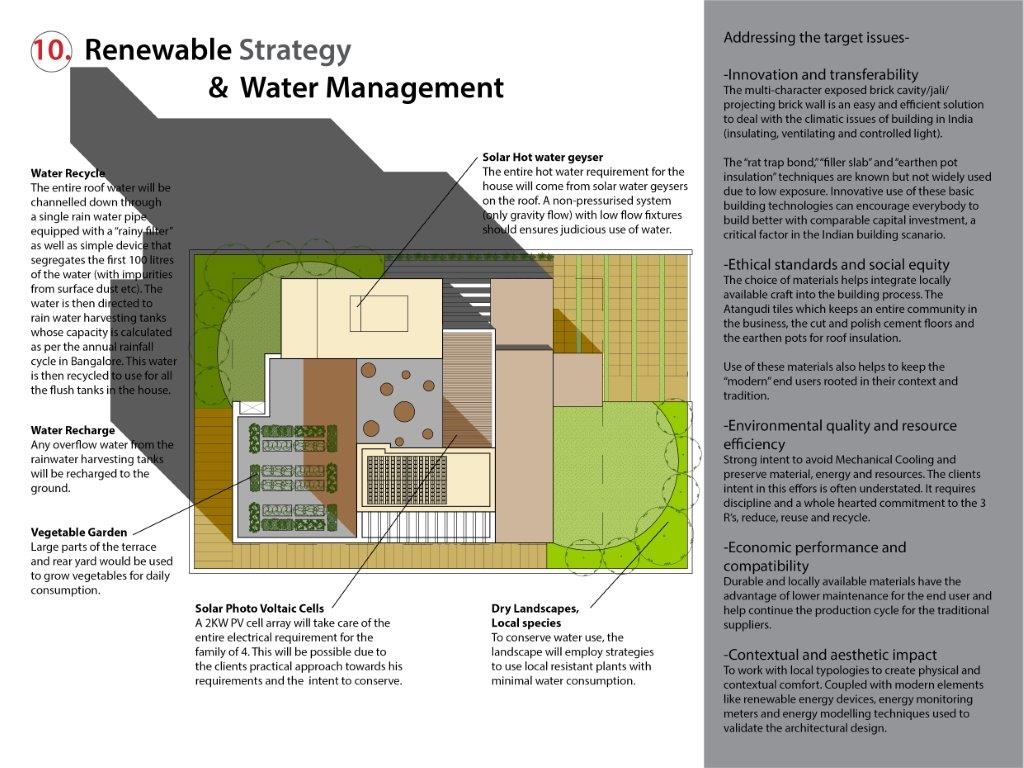
Renew/Recycle: Rainwater recycled into the flush tanks and for landscape using local species. Solar water heaters and PV cells for 100% power generation from renewable sources.
-Innovation and transferability
The multi character exposed brick Cavity/Jali/Projecting brick wall is an easy and efficient solution to deal with the climatic issues of building in India (insulating, ventilating and controlled light). The “rat trap bond,” “filler slab” and “earthen pot insulation” techniques are known but not widely used due to low exposure.
-Ethical standards and social equity
The choice of materials helps integrate locally available craft into the building process, the Atangudi tiles which keeps an entire community in the business, the cut and polish cement floors and the earthen pots for roof insulation. It also helps to keep the “modern” end users rooted in their context and tradition.
-Environmental quality and resource efficiency
Strong intent to avoid Mechanical Cooling and preserve material, energy and resources.
-Economic performance and compatibility
Durable and locally available materials have the advantage of lower maintenance for the end user and help continue the production cycle for the traditional suppliers.
-Contextual and aesthetic impact
To work with local typologies to create physical and contextual comfort. Coupled with modern elements like renewable energy devices, energy monitoring meters and energy modelling techniques used to validate the architectural design.




Leave a Comment